Have you ever wondered why some websites always appear at the very top of Google’s search results while others never get noticed? It’s not magic—it’s the power of smart on page SEO. In today’s competitive digital world, improving your visibility on search engines is not optional; it’s a necessity. And the first step is optimizing the elements you control directly on your own website.
on page SEO is like the backbone of your content’s success. It helps search engines understand what your page is about, who it benefits, and why it deserves to rank higher than millions of other pages. When done correctly, it improves both your content quality and user experience—two things Google values the most.
By using effective on page SEO strategies such as optimizing your title tags, creating clear header structures, writing keyword-rich content, improving page loading speed, and ensuring mobile responsiveness, you give your website the best chance to appear at the top of SERPs. The best part? You don’t need complex tools or advanced skills. With consistent optimization and a user-first mindset, ranking becomes much easier than you think.
So yes—those top-ranking websites didn’t get there by accident. They used strong on page SEO techniques, and you can too. With the right approach, your website can reach the front page and attract more traffic every day.
What is On Page SEO Elements
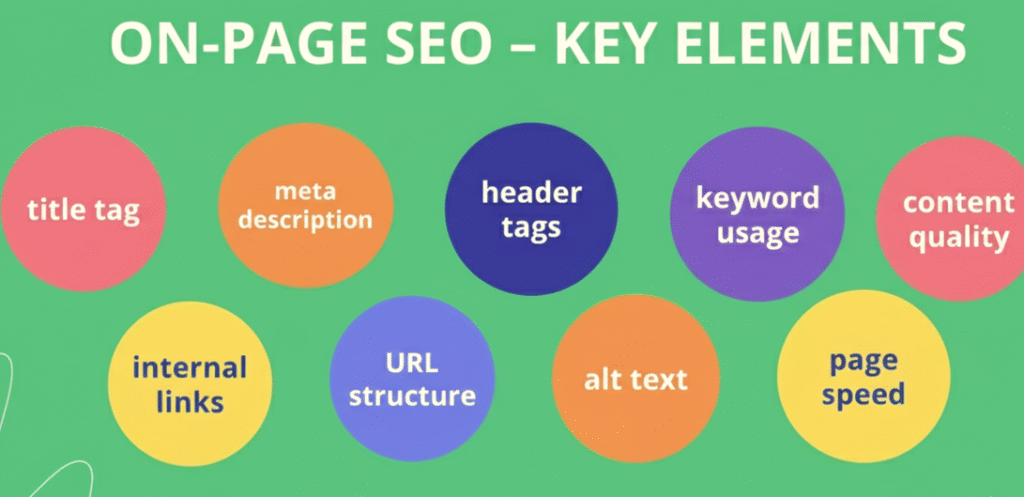
on page SEO refers to all the optimization techniques you apply directly on your website’s pages to help them rank higher in search engine results. It means improving your page content, HTML code, titles, headings, images, URLs, and every element that helps search engines understand your website better.
When Google crawls your page, it checks what the page is about, how useful the information is, and whether it satisfies the user’s search intent. The main goal of on-page SEO is to make your content meaningful, well-structured, and easy for both users and search engines to understand.
Important on page SEO elements include using the right keywords, writing engaging title tags, creating clear meta descriptions, organizing content with proper H1/H2/H3 headings, and keeping URLs clean and readable. Fast loading speed, mobile responsiveness, optimized images, and helpful internal links also play a key role in on page SEO.
In simple words, on page SEO is like building a strong foundation for your website. If the structure, content, and user experience are well-optimized, Google will trust your page more and rank it higher in search results.
A well-optimized page not only improves your website’s visibility but also helps users find exactly what they are looking for—making it a win-win for both search engines and visitors.
1. title tag
A title tag is one of the most essential on page SEO elements that defines what a webpage is about. It is placed inside the <head> section of the HTML code using the <title> element. This short line of text appears in multiple important places: as the blue, clickable headline in Google search results, as the label shown on browser tabs, and as the text that appears when someone shares your page on social media or bookmarks it. Because of this visibility, the title tag plays a major role in helping both users and search engines quickly understand the purpose and topic of the page.
The primary function of a title tag is to summarize the page content in a clear, concise, and meaningful way. It sets the expectation for users even before they visit the page. A well-crafted title tag influences whether a user decides to click on your page or scroll past it, making it directly connected to improving click-through rates (CTR). For search engines, the title tag acts as a strong relevance signal. It tells Google which keywords and subjects are most important on that page, helping the algorithm determine when and where the page should appear in search results.
From an on page SEO perspective, optimizing the title tag is crucial. Best practices suggest keeping it under 60 characters so it displays properly without being cut off. Including your primary keyword near the beginning of the title tag is also recommended, as it helps search engines understand your content’s core topic. A compelling and descriptive title, combined with natural keyword placement, can significantly boost visibility and ranking.
Overall, a title tag is the webpage’s main headline for the entire internet. It impacts discoverability, user experience, and SEO performance. When written effectively, it helps attract the right audience, increases organic clicks, and strengthens the overall value of your content in search engines.
2. meta description
A meta description is a short but powerful element of on page SEO, designed to give users a quick preview of what a webpage contains before they even visit it. Although it’s not displayed on the webpage itself, it is added in the HTML code as a meta tag and often appears as the snippet that shows up under the title tag in search engine results. This small block of text plays a major role in influencing user behavior, helping people decide whether to click on your link or scroll past it.
The main purpose of a meta description is to summarize the content of the page in a clear, concise, and engaging way. When users read this description in search results, it should give them enough information to understand what the page is about while also encouraging them to visit it. Even though search engines like Google sometimes replace the written meta description with a snippet of their own choosing from the page content, writing an optimized one is still very important because it gives you the opportunity to shape how your page is presented in search results.
While meta descriptions are not a direct ranking factor, they significantly impact CTR (Click-Through Rate). A strong, well-written description can attract more clicks, which indirectly supports better performance in search rankings. Meta descriptions can also appear in social media previews when your link is shared, making them a valuable part of user experience and digital visibility.
To make a meta description effective, it should be unique for every page, reflect the main idea of the content, and be written within the recommended length of 50–160 characters. Including target keywords helps match user search queries and increases relevance. Adding persuasive language and a clear call to action—such as “Learn more,” “Explore now,” or “Get started”—makes the description more compelling and encourages users to engage. In essence, a good meta description acts as a mini-advertisement for your page, strengthening both your SEO and your overall online presence.
3. URL
A URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is a unique address used to identify and access resources on the internet, such as web pages, images, videos, or files. Commonly known as a web address or link, it tells a web browser exactly where a resource is located and how to retrieve it. When a user types a URL into the browser’s address bar or clicks on a hyperlink, the browser uses that URL to connect to the correct server and fetch the requested content.
A URL is made up of several important components, starting with the protocol, such as http or https. The protocol defines how data will be transferred between the browser and the server. HTTPS is the secure version, offering encrypted communication for better safety. Next comes the domain name, which identifies the specific website or server, like google.com or example.org. This part tells the browser which server to contact. Following the domain is the path, which indicates the exact location of a file or page on the server—such as /blog/article.html or /images/photo.jpg. The path can include multiple subdirectories, separated by forward slashes (/), showing the structure of folders and files on the website.
URLs can also include optional components, such as parameters and anchors. Parameters appear after a question mark (?) and are used to send additional information, like search queries or filters—for example, ?id=10 or ?search=books. Anchors, identified by a hash symbol (#), direct the browser to a specific section within a webpage, such as #contact or #reviews.
For example, in the URL https://aiseohubtech.com/ai-seo/
- https:// is the protocol
- www.aiseohubtech.com is the domain name
- /page/about.html is the path to the specific resource
In essence, a URL acts as the internet’s addressing system. It provides clear instructions for locating and accessing digital resources, making web navigation possible. Without URLs, the internet would have no reliable way to connect users with the content they want to reach.
4. H1

In web development, H1 is an HTML tag used to define the main heading or primary title of a webpage. It represents the most important heading on the page and helps search engines like Google understand the central topic and purpose of the content. Because of this, the H1 tag plays a crucial role in on page SEO. When an H1 is written correctly and meaningfully, it improves the page’s clarity and helps search engines interpret the content more effectively, which can ultimately boost search visibility.
Overall, the term H1 has multiple meanings depending on the context. While it is a key HTML element in web development, it also refers to a Hyundai van model in the automobile industry, and in immigration it relates to the H-1B visa category for specialized occupations. Despite sharing the same name, each meaning belongs to a completely different field—web development, automobiles, and immigration—giving H1 a distinct identity in each area.
5. H2/H3

Many experts suggest using heading tags in a clear and organized hierarchy to keep your webpage structure clean and easy for both users and search engines to understand. According to best practices, the H1 tag should be used only once on a page and reserved exclusively for the main title. This helps search engines easily identify what the page is primarily about. After that, H2 tags are ideal for major sections or key topics within the content, creating a natural flow and breaking the page into readable parts. For topics that fall under those main sections, H3 tags serve as subheadings, offering an even deeper level of structure.
Using heading tags properly not only improves on page SEO but also enhances user experience by making the content easier to scan and navigate. When it comes to indenting text for quotations, specialists recommend avoiding the use of UL (unordered list) tags, as they are meant for listing items, not for styling text. Instead, the BLOCKQUOTE tag is the correct and semantic choice for quotes. It clearly communicates to browsers and search engines that the text is a quotation, maintaining both accuracy and accessibility in your HTML structure.
6. keyword

Keywords are the words or phrases people type into Google or any search engine to find information. For example, if someone wants to buy a jacket and searches for “men’s leather jacket”, that entire phrase becomes their keyword. A keyword can be a single word or a group of words. Google uses these keywords to understand what the user wants and then shows the most relevant websites. In this way, keywords play an important role in helping users find the right information quickly.
7. LSI Keywords

LSI keywords are words or phrases that are related in meaning to your main keyword. They are not synonyms, but they belong to the same topic. Search engines use these related terms to understand what your content is actually about.
Example:
If your main keyword is “coffee,” then LSI keywords can be:
caffeine
beans
roast
espresso
All these words are connected to coffee, so Google understands the context of your content.
How LSI works:
Take the word “apple” as an example:
- If your content includes words like orchard, fruit, pie → Google knows you mean the fruit “apple.”
- If you mention iPhone, MacBook, technology → Google understands you are talking about Apple (the company).
This helps search engines identify the correct meaning.
Why LSI keywords are important for on page SEO:
✔ They help search engines understand the real context of your content
✔ They make your content more relevant and useful
✔ They prevent keyword repetition (keyword stuffing)
✔ They help improve your ranking because your content looks natural and informative
In simple words:
LSI keywords make your article clearer, more meaningful, and more helpful for both Google and your readers.
8. content
Content simply means anything that is inside something. It can be information, items, ingredients, online material, or even your feelings. For example, the text inside a book, the data on a website, or the ideas in a video are all called content. If you look inside a bag or box, the things you find are also called its contents. In food or drinks, content refers to how much of a specific ingredient is present, like sugar content or fat content.
In the digital world, content includes blog posts, videos, reels, images, podcasts, and anything shared online to inform or entertain people. The word can also describe a feeling. When someone is satisfied and happy with what they have, they are said to be “content.”
So in simple words, content is everything that fills something—whether it’s information, objects, ingredients, digital material, or emotions. It is what gives meaning and value to anything.
9. internal links
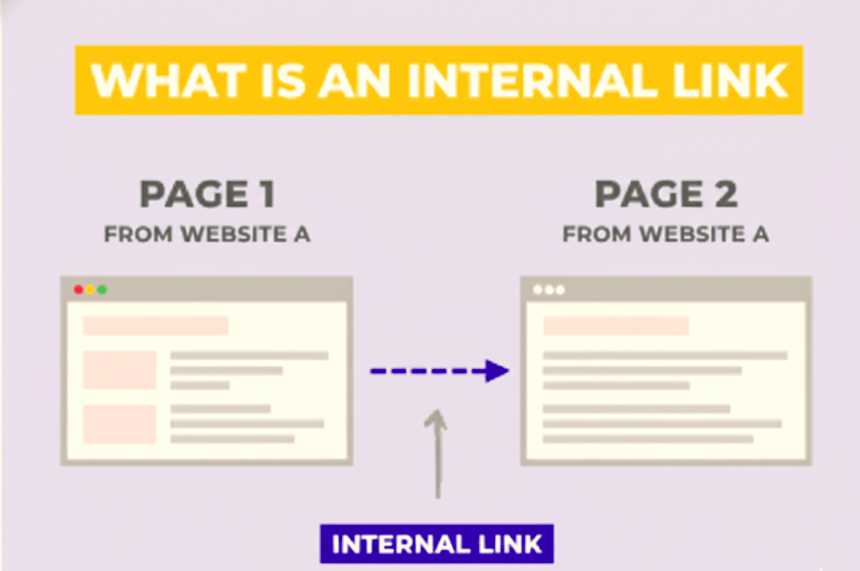
Internal links are links that take you from one page of a website to another page on the same website. They help users move around the site easily and also help Google understand your website better.
Why internal links are important
1. Help users navigate
Internal links guide visitors from one page to another.
Example: Links in the menu like “Home,” “About Us,” “Blog,” etc.
2. Help Google crawl your site
Search engines use internal links to find new pages and understand how your website is organized.
3. Improve SEO
Internal links tell Google which pages are important and help pass “link juice” (PageRank) to other pages.
4. Keep users engaged
When you add links inside your content to related articles, users stay longer on your website.
Examples of internal links
- Menu links: Like “Home,” “Services,” or “Contact.”
- Contextual links: Inside an article, like linking “weight loss tips” to another article on “healthy meals.”
- Breadcrumbs: The small navigation path at the top of a page, like Home > Blog > Tips.
In simple words:
Internal links help users and Google move around your site smoothly and understand your content better.
10. Image Alt Text
Image alt text is a short description written for an image on a webpage. It helps two main things:
- Accessibility – so blind or visually impaired users can understand the image through screen readers.
- SEO – so Google can understand what the image is about.
Search engines and screen readers cannot “see” images, so alt text tells them what the image shows.
Why image alt text is important
1. For Accessibility
- Screen readers read the alt text aloud to users who cannot see the image.
- If an image does not load, alt text appears instead, so users still understand the content.
2. For SEO
- Google uses alt text to understand and index images.
- Good alt text helps your images appear in Google Image Search.
- You can add keywords naturally, but don’t overuse them (no keyword stuffing).
How to write good alt text
- Be specific: Describe what the image clearly shows.
Example: Instead of “plant,” write “tomato plant growing in a pot.” - Keep it short: Around 125 characters is enough.
- Describe the context: Explain why the image is used.
Example: “Businesswoman holding a coffee cup in an office.” - Be honest: Don’t add keywords that don’t match the image.
- If image is decorative: Use
alt=""so screen readers skip it.
In simple words: Alt text tells Google and screen readers what an image shows. It makes websites accessible and helps improve SEO.
Benefits of Using Tools to Optimize on page SEO
1. Saves Time and Effort
SEO tools automate tasks like keyword research, meta tag creation, and content analysis. Instead of manually checking everything, you get instant insights in minutes.
2. Improves Content Quality
Tools highlight issues such as keyword stuffing, missing headings, low readability, or poor structure. This helps you create high-quality, user-friendly content.
3. Better Keyword Optimization
On-page SEO tools suggest the right keywords, LSI terms, and keyword density so your content ranks higher without over-optimization.
4. Fixes Technical Issues Fast
Tools detect problems like broken links, missing alt tags, duplicate content, slow page speed, and incorrect indexing — helping you improve SEO health.
5. Enhances User Experience (UX)
When you optimize speed, design, headings, and readability, the user experience becomes smooth — leading to higher engagement and lower bounce rates.
6. Increases Search Engine Rankings
With proper keyword placement, optimized meta tags, and technical improvements, your pages become more search-friendly and rank higher on Google.
7. Helps You Beat Competitors
Tools show competitor keywords, content gaps, and ranking strategies, allowing you to create more powerful and complete content.
8. Provides Accurate Data & Insights
SEO tools offer real-time analytics, keyword performance, page-level SEO scores, and recommended changes — ensuring every decision is data-driven.
9. Guides Beginners Easily
Even if you are new to on page SEO, tools act like a step-by-step guide — showing what to fix and how to improve each page.
10. Boosts Organic Traffic
When your pages are well-optimized, keyword-rich, and technically strong, organic traffic increases automatically.
On-Page SEO vs Off Page SEO difference (Column Format)
| Category | On-Page SEO | Off-Page SEO |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Meaning | Improving things inside your website to boost ranking. | Building authority outside your website to increase trust and visibility. |
| What It Focuses On | Content quality, keywords, technical setup, user experience. | Backlinks, reputation, social signals, brand presence. |
| Definition | Optimizing factors on your own website to improve search rankings and user experience. | Building credibility and authority through activities that happen outside your website. |
| Main Goal | Make content easy for Google and users to understand. | Make Google trust your website as an authority. |
| Key Elements | – Content quality & keyword usage – Meta tags & headings – Internal linking – Page speed & mobile friendliness – URL optimization | – Backlink building from trusted websites – Social media engagement – Guest blogging – Brand mentions |
| Where It Happens | Inside your website | Outside your website |
| Why It Matters | Helps search engines understand your website clearly. | Shows search engines that your website is trustworthy and popular. |
| Result | Better user experience + improved content structure. | Higher authority + stronger rankings. |
| Need Both? | Yes | Yes |
| Reason | On-page makes your website strong internally. | Off-page makes your website strong externally. |
Why Is On Page SEO Important?
On-page SEO is essential because it helps Google understand your website, improves user experience, and boosts your search rankings. It includes everything you optimize inside your website—like content, headings, keywords, URLs, images, and page speed.
Below are the main reasons why on page SEO matters:
1. Helps Google Understand Your Content
When you use proper keywords, headings, titles, and meta descriptions, Google easily understands what your page is about. This directly improves your chances of ranking higher.
2. Improves Search Ranking
Good on page SEO makes your website more relevant and organized. This increases the chances of your page appearing at the top of search results.
3. Better User Experience
On-page SEO ensures your site is fast, clean, and easy to read.
Examples:
- Fast loading pages
- Mobile-friendly layout
- Proper content structure
Happy users = better SEO.
4. Increases Organic Traffic
When Google understands your content and ranks it higher, your site gets more organic traffic without paying for ads.
5. Builds Trust and Authority
High-quality content, clear headings, internal linking, and strong meta tags help create trust with both Google and users. It makes your site look professional and reliable.
6. Improves Conversions
If users can find information easily and your website loads quickly, they are more likely to take action—like buying a product, signing up, or visiting more pages.
7. Long-Term Benefits
Good on page SEO provides long-lasting results. You don’t need to update it daily, but it continues to bring traffic and better rankings over time.
conclusion
On page SEO is the backbone of any successful website. It helps search engines clearly understand your content and gives users a smooth, enjoyable experience. When your pages are well-optimized—with the right keywords, strong titles, proper headings, clean URLs, fast loading speed, and helpful internal links—your website naturally ranks higher and attracts more visitors.
Strong on-page SEO not only improves visibility but also builds trust, increases engagement, and boosts conversions. It delivers long-term results without relying on paid ads. In short, if you want sustainable growth, higher rankings, and better user satisfaction, mastering on-page SEO is essential.
12 FAQs About on page SEO
1. What is on page SEO?
on page SEO means optimizing the content and elements on your website so search engines can understand and rank it better.
2. Why is on page SEO important?
It helps your site become more visible, improves user experience, and increases your chances of ranking on Google.
3. What are the main elements of on page SEO?
Title tags, meta descriptions, keywords, headings, URLs, internal links, images, and page speed.
4. How many keywords should I use on page SEO?
Use 1 primary keyword and a few related (LSI) keywords naturally—avoid keyword stuffing.
5. Does Google still use keywords?
Yes, but it focuses more on search intent and content quality rather than just exact keywords.
6. What is a meta description?
A short summary of your page that appears in Google search results and encourages users to click.
7. What is the role of headings in SEO?
Headings (H1, H2, H3) help organize your content and make it easy for users and search engines to understand.
8. Does URL structure affect SEO?
Yes. Short, clear, and keyword-rich URLs perform better in search results.
9. What is internal linking?
It means linking one page of your site to another page. It helps users navigate and helps Google crawl your site.
10. Should I optimize images for SEO?
Yes. Use descriptive image alt text and compress images to improve loading speed.
11. Does mobile-friendliness matter for SEO?
Absolutely. Google prefers mobile-responsive websites and ranks them higher.
12. How often should I update my content?
Update important pages every 3–6 months to keep them fresh, relevant, and SEO-friendly.

